DESIGNS
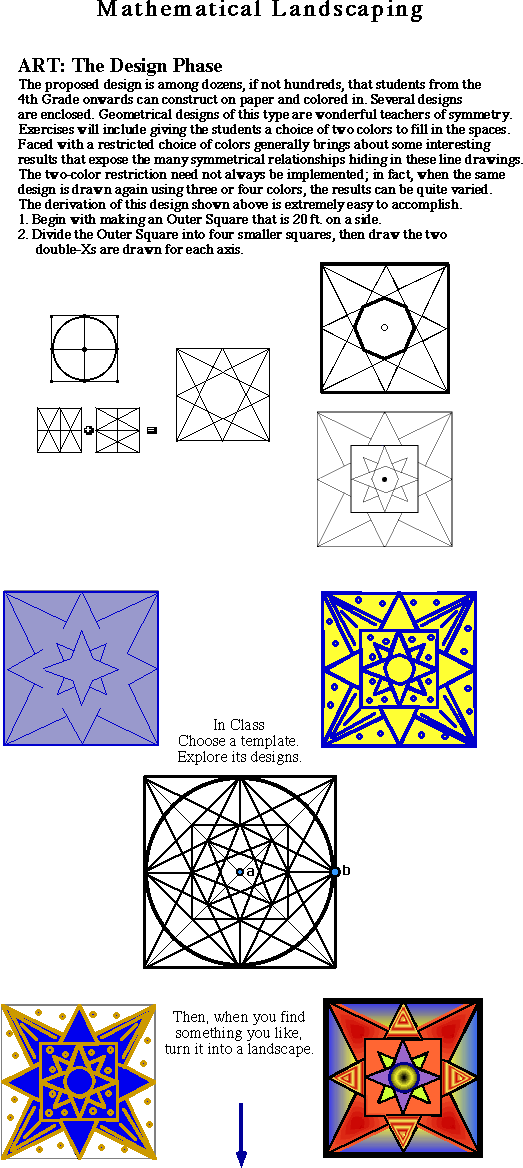

|
FUNCTIONING GARDEN
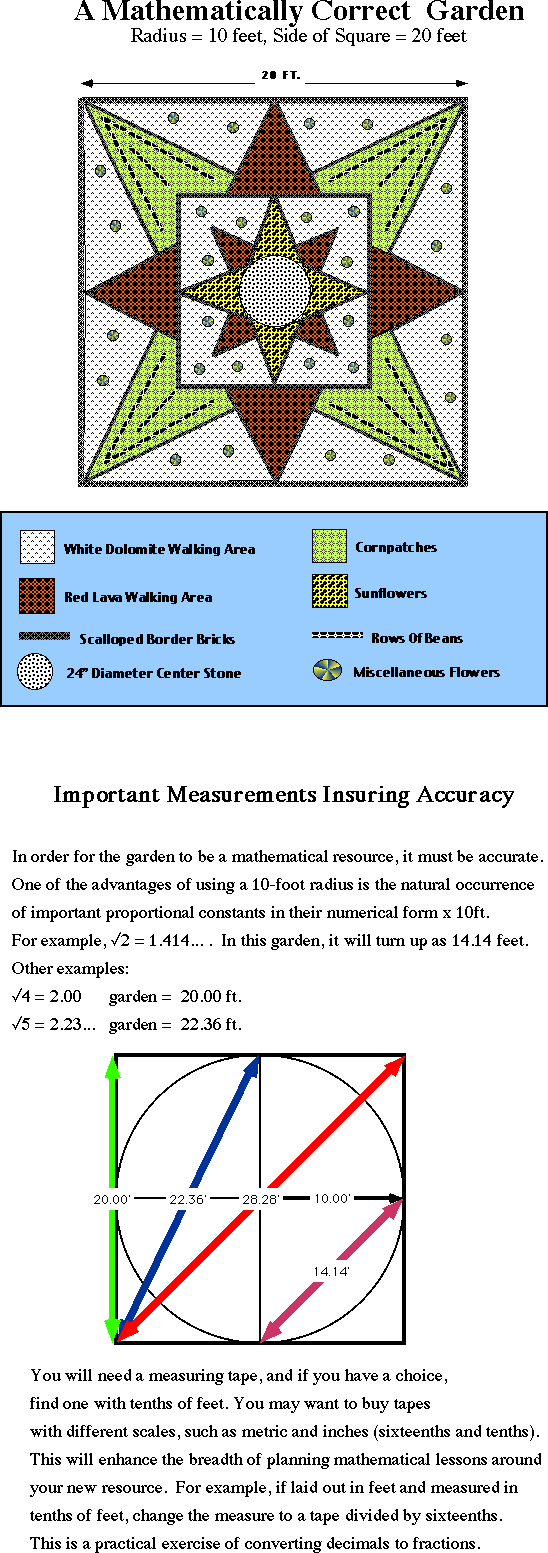
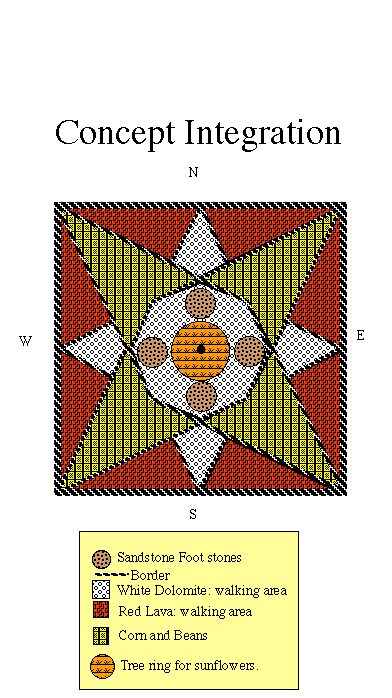
1. The 20ft x 20ft garden design is based upon the internal geometry of the square. The design will be constructed with 24" scalloped bricks that are 5" high and about 2" thick. Bricks can be used to form the perimeter, but I have found that railroad ties help reduce the intrusion of unwanted flora. The bricks are the backbone of the design, but they can also be rearranged into other designs by teachers and/or students. These designs can be worked out in the classroom and then applied outdoors. 2. Corn and beans will be the primary crop. In prehistoric America, this pair was usually grown together or consecutively because, as corn depletes nitrogen from the soil, beans replace it through their natural chemical interaction with the soil. Old corn stalks also contain some nitrogen and these can be broken up an returned to the soil as well. Sunflowers are planned for the central octagonal area in circular bricks; four smaller rings can represent smaller patches of sunflowers or circular stepping stones. Wild flowers will be spread about in areas outside the corn-bean patch. Lava (vesicular basalt gravels) and the central area will serve to access the corn bean patch for watering and cultivation. A three-inch base of sand will underlie the lava and dolomite; chicken mesh ‹ preferably two layers between sand, acts as an anti-gopher measure. Students will gain a practical appreciation of symbiotic concepts such as theory and practice, blueprints and physical construction, beauty and growth.
CARDINAL DIRECTIONS
GEOLOGY
|
Contact
E-mail: Chris Hardaker
Copyright 1994-2000, Chris Hardaker